2D-Echo ( Echocardiogram )
An echocardiogram is an ultrasound test that checks the structure and function of your heart. An echo can diagnose a range of conditions including cardiomyopathy and valve disease.
What is an echocardiogram?
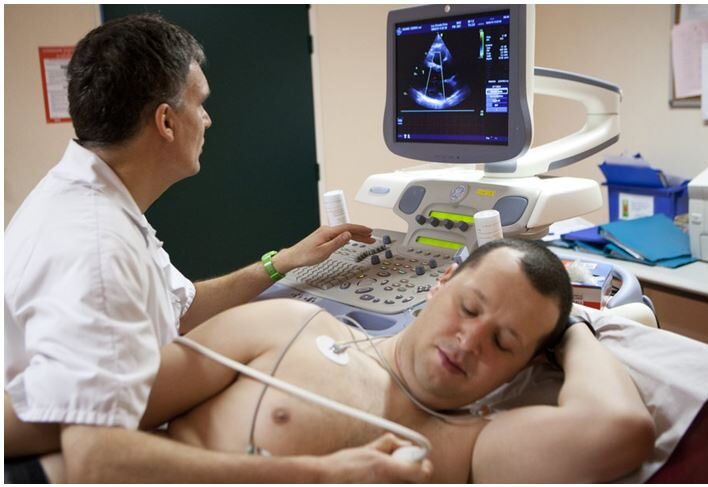
An echocardiogram (echo) is a graphic outline of your heart’s movement. During an echo test, your healthcare provider uses ultrasound (high-frequency sound waves) from a hand-held wand placed on your chest to take pictures of your heart’s valves and chambers. This helps the provider evaluate the pumping action of your heart.
Providers often combine echo with Doppler ultrasound and color Doppler techniques to evaluate blood flow across your heart’s valves.
Echocardiography uses no radiation. This makes an echo different from other tests like X-rays and CT scans that use small amounts of radiation.
When would I need an echocardiogram?
Your provider will order an echo for many reasons. You may need an echocardiogram if:
- You have symptoms, and your healthcare provider wants to learn more (either by diagnosing a problem or ruling out possible causes).
- Your provider thinks you have some form of heart disease. The echo is used to diagnose the specific problem and learn more about it.
- Your provider wants to check on a condition you’ve already been diagnosed with. For example, some people with valve disease need echo tests on a regular basis.
- You’re preparing for a surgery or procedure.
- Your provider wants to check the outcome of a surgery or procedure.

